As the proportion of new energy continues to increase, renewable energy such as wind power and photovoltaics has brought huge challenges to the stability of traditional power grids due to its intermittent and volatile characteristics. Therefore, new power system applications have emerged. In order to ensure the safe, stable and efficient operation of the power system, the energy storage system has become one of the core supporting technologies of the new power system. Energy storage can not only reduce peak loads and fill valleys, improve the efficiency of electric energy utilization, but also improve the ability to absorb new energy, promote power grid frequency regulation and peak load regulation, and even participate in power market transactions, providing key support for building a more flexible, intelligent and sustainable energy system.
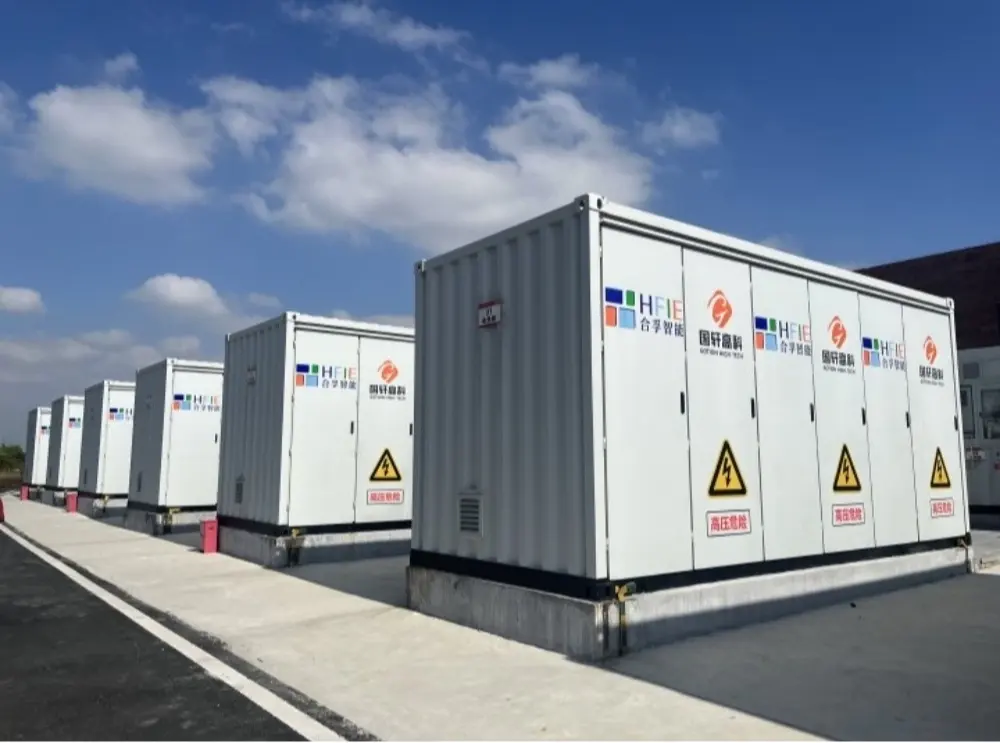

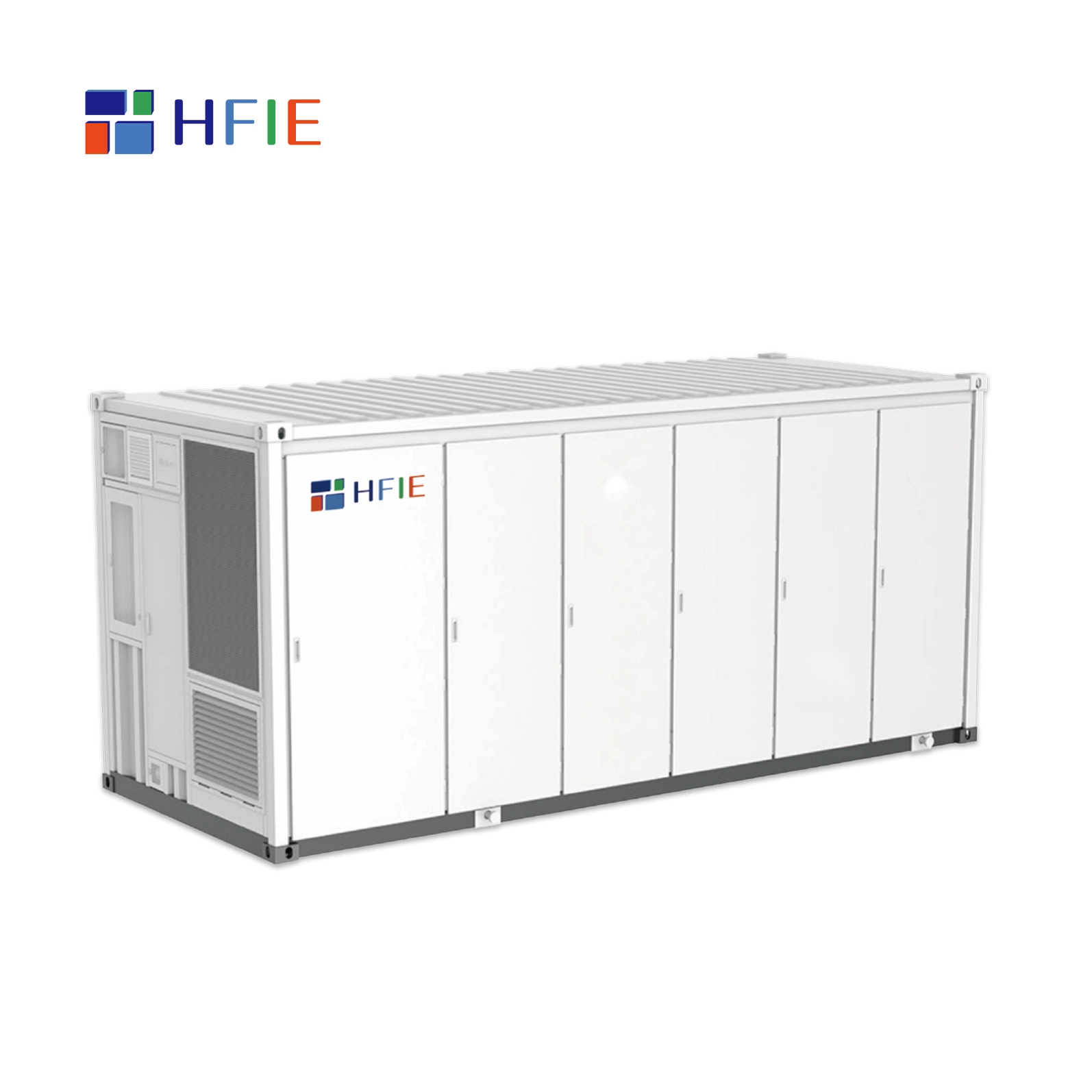
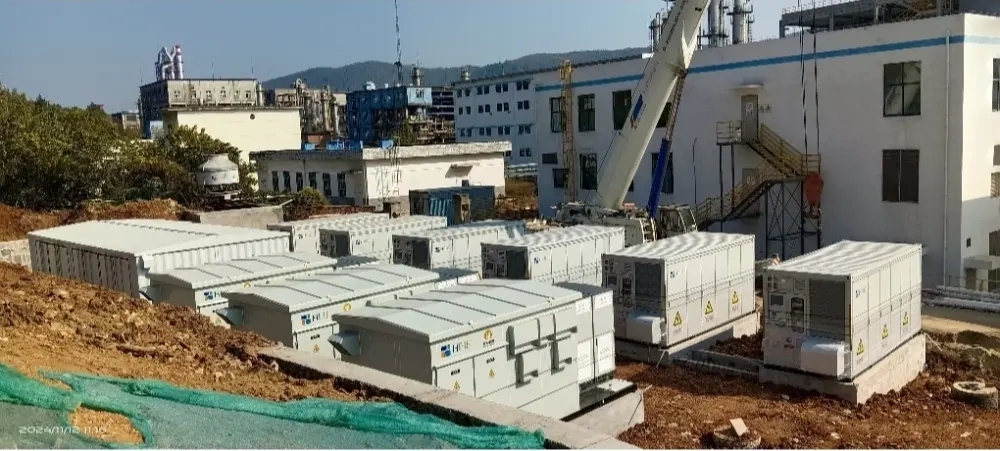
Basic components of energy storage system
Energy storage unit (core equipment): responsible for the storage and release of electric energy, equivalent to “power warehouse”. Common types: Electrochemical energy storage: lithium-ion battery (lithium iron phosphate, ternary lithium), sodium-ion battery, all-vanadium liquid flow battery, etc. Pumped storage, compressed air energy storage, flywheel energy storage. Thermal energy storage: molten salt energy storage, phase change material energy storage, etc. Among them, lithium-ion batteries have become the mainstream energy storage technology due to their high energy density, fast response speed and strong adaptability.
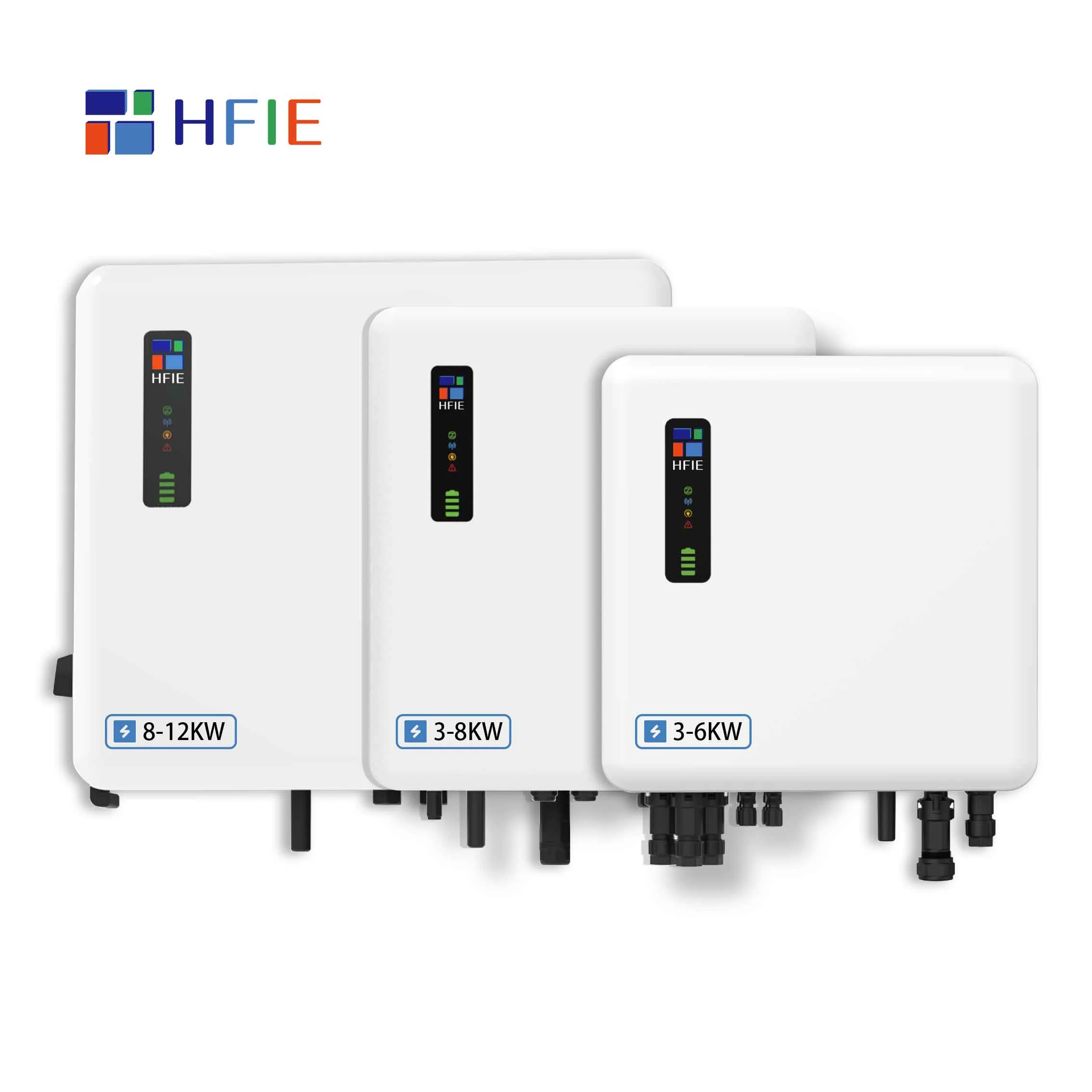
Energy storage converter (PCS): responsible for the conversion of electric energy, converting alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC) for storage, or inverting DC into AC for grid connection. Control the charging and discharging process of the battery to ensure efficient operation of the system. Participate in grid frequency regulation and peak regulation, and provide auxiliary services such as reactive power compensation.

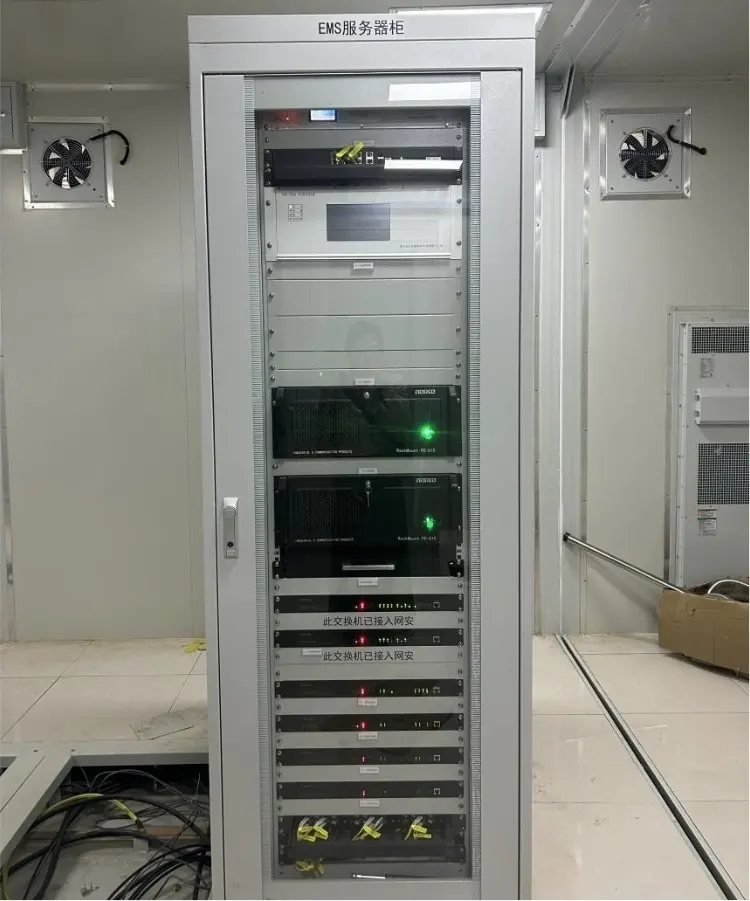
Energy management system (EMS) is responsible for the coordinated control of the entire energy storage system, equivalent to the “brain”. Real-time monitoring of battery status (SOC, SOH, etc.) to optimize charging and discharging strategies. Combine electricity prices and electricity demand to develop the optimal energy scheduling plan. Use AI algorithms to predict load demand and improve system operation efficiency.

Battery Management System (BMS): Manage battery cells and battery modules to ensure safe operation. It is mainly responsible for monitoring battery temperature, voltage, and current to prevent overcharging and over-discharging. Balance each battery module to extend battery life. Provide fault warning to prevent thermal runaway and fire.
Transformer and distribution system: Connect the energy storage system to the power grid to ensure safe and efficient transmission of electricity.